
How Long Will Artemis 2 Be in Space?
The process of sending NASA back to the Moon today is no longer a distant dream — it’s actually happening and is an unfolding reality. This recharged effort is being driven by the Artemis space program.
It is setting its sights on returning people to the Moon. The plan is to establish a long-term presence there and prepare to run missions in Damages. Its most anticipated missions include Artemis 2, the first manned flight of the Artemis era.
A common address among space fans, instructors, and trying space travelers is: how long will Artemis 2 be in space? The reply uncovers not a mission timeline, but moreover NASA’s cautious, systematic approach to human space exploration.
Understanding Artemis 2 In Context
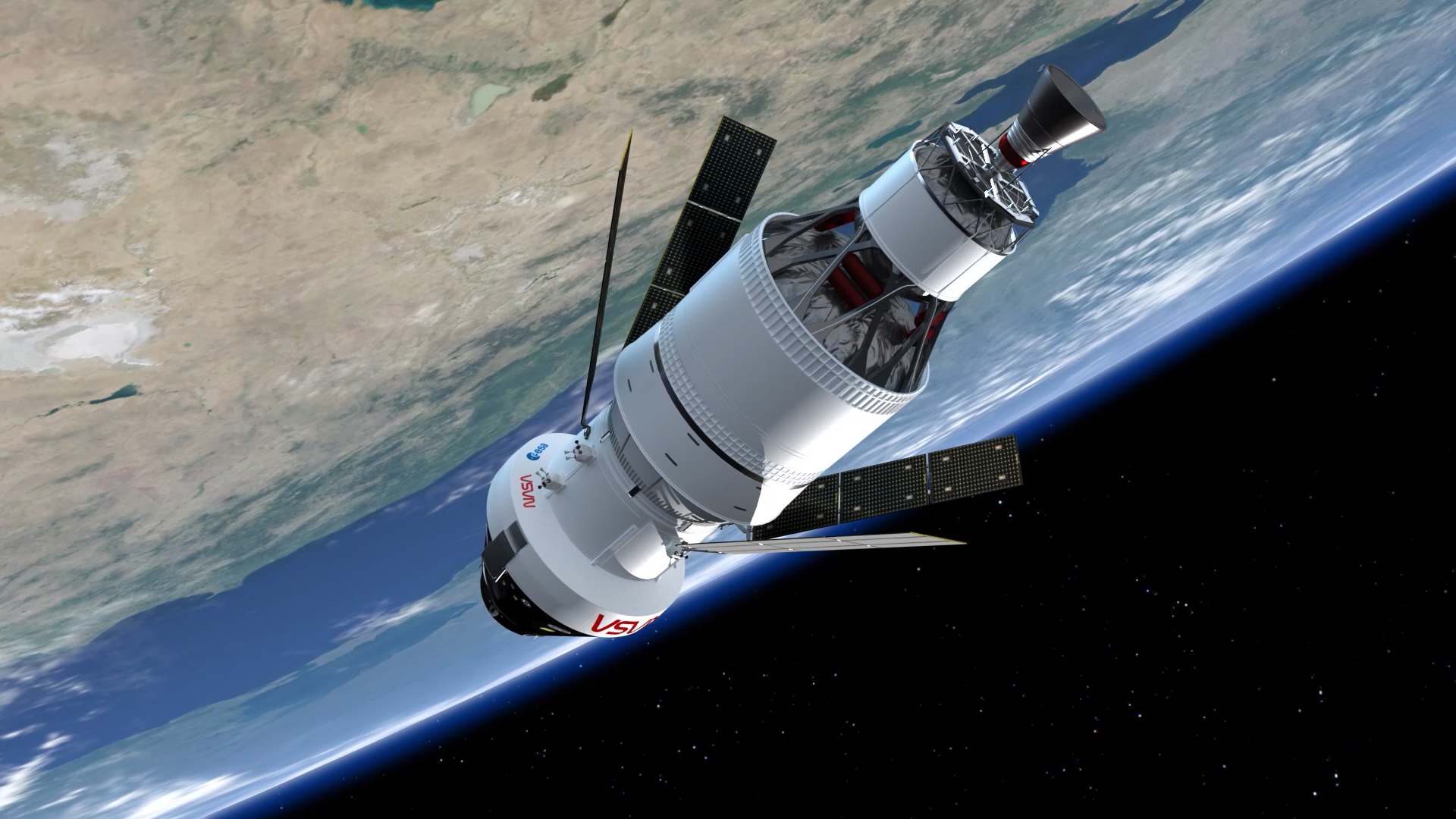

Before talking about mission term, let’s see at how Artemis 2 fits into the bigger Artemis program. Artemis 1 (completed) was an uncrewed test flight that sent the Orion shuttle around the Moon and back to Earth.
Read Also: Pentagon Tech Hub to Launch Dozens of New Projects With FY24 Funding
Artemis 2 will be the to begin with mission with space explorers. It will test life-support frameworks, route, and shuttle execution in profound space. Artemis 3 is also scheduled to land astronauts on the lunar surface for the first time since Apollo 17.
Artemis 2 is not landing on the moon. Instep, it’s a kind of proving ground — to ensure that equipment as well as people are ready for future landings.
The Artemis 2 Timeline In terms of the timeline for Artemis 2, apparent to everyone there will be a mission days (24-26 hours) that relies on the SLS and Orion to put humans in distant orbit.
So Then, How Long Will Artemis 2 Spend In Space?
NASA estimates that Artemis 2 will last about 10 days, from launch to splashdown. This length finds a cautious adjust. It's long sufficient to test manned shuttle frameworks. But it's also brief sufficient to keep dangers moo in this early mission. We anticipate the mission timeline to see generally like this:
- Day 1: Dispatch on board the Space Dispatch Framework (SLS)
- Days 2–3: Travel from Soil to the Moon
- Days 4–6: Lunar flyby and deep-space operations
- Days 7–9: Return travel to Earth
- Day 10: Reentry and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean
The 10-day window is presently the common gauge. Correct timings might alter as mission arranging develops.
Why 10 Days Is the Sweet Spot?
Ten days may feel short after months on the Universal Space Station. But for a mission to deep space, it has significance. First, Artemis 2 will take astronauts farther from Earth than humans have gone since Apollo.
There’s no quick protect option, unlike the moo Soil circle missions. Every system — from command and impetus to waste management — must operate seamlessly.
Second, NASA is in a position of testing human endurance in deep space without unnecessary exposure to radiation and isolation. A 10-day mission gives sufficient time to check:
- Crew wellbeing and performance
- Life-support framework reliability
- Communications delays
- Navigation exactness past Earth's orbit
This kind of information is crucial before longer missions start. This includes lunar surface remnants, and Defaces transit.
The System For The Space Dispatch Part
One big factor in mission length is the rocket. Artemis 2 is set to launch on the most powerful rocket NASA has ever built, called the Space Launch System (SLS).
You Must Also Like: Why SpaceX Starlink Satellites Are All Over the Sky Right Now?
The SLS was designed by engineers to launch massively large payloads and on a trajectory that ducked shuttle past soil circle in one flight. It plays a pivotal role not only in Artemis 2’s success, but the entire Artemis space program.
Oddly enough, hype regarding the SLS has in fact bled over into popular culture. Instructional toys like NASA Artemis Lego sets are great for teaching rocket design, mission planning and space history.
They are available to both kids and adults. These models appear the colossal and complex nature of the SLS. They clarify how it can bolster missions like Artemis 2.
What Will Space explorers Do Amid Those 10 Days?
Although Artemis 2 won’t include a lunar landing, the group will be anything but idle.
Key exercises amid the mission include:
Testing life-support frameworks: oxygen era, carbon dioxide expulsion, temperature control, and water recycling.
Navigation Works out: Checking Orion's capacity to explore profound space without continuous ground support.
Manual flight tests: Space travelers will physically control the shuttle to guarantee it reacts as expected.
Radiation observing: Measuring radiation introduction past Earth’s defensive magnetosphere.
Crew operations: Assessing resting, eating, and working schedules in profound space.
These errands help NASA in surveying Orion's status for longer, more complex missions.
The Lunar Flyby: A Basic Moment
One of the most sensational minutes of Artemis 2 will be its lunar flyby. The shuttle won’t enter lunar circle. Instep, it will circle around the Moon. It will utilize the Moon's gravity to slingshot back toward Earth. This move finishes a few goals:
- Tests high-speed route close the Moon
- Demonstrates Orion’s capacity to work distant from Earth
- Provides breathtaking sees and priceless imaging data
The shuttle won't remain close the Moon for long. Still, this stage is key to the mission's reason. It moreover plays a enormous part in the 10-day duration.
Training for Artemis 2: Test systems and Preparation
Behind the scenes, space travelers spend a long time planning for a mission that endures 10 days. One of the apparatuses included in this arrangement is progressed reenactment technology.
The Artemis space bridge test system trains space travelers and mission controllers. It appears how progressed these frameworks can be. These test systems mirror mission timelines, shuttle activities, and crisis circumstances. Groups can hone everything from typical errands to worst-case failures.
This preparing makes a difference the group make the most of each diminutive amid the 10-day mission. It centers on productivity and safety.
How Artemis 2 Compares to Apollo Missions?
Many individuals make comparisons between Artemis 2 and missions from the Apollo period. Apollo 8, for case, was the to begin with manned mission to circle the Moon and kept going around 6 days. In Comparison:
- Artemis 2 is longer than Apollo 8
- Artemis 2 voyages comparable separations but with present day technology.
- Artemis missions emphasize maintainability and future expansion.
The longer term appears advanced mission objectives. It incorporates more framework testing and centers more on group wellbeing and information collection.
Why Mission Length Matters for the Future?
The 10-day duration of Artemis 2 is there for a reason and isn’t just picked out of thin air — it’s a stepping stone. The information collected during the course of this mission will have bearing on:
Duration of Moon Missions In briefGNUCIDL-3GNUFNT If you participate_ Init Structure, then this section should contain information on the length of future lunar missions.
What is the optimal mission duration that spacefarers can safely spend in lunar orbit. The Defaces missions planned to last months or even years.
Knowing how long Artemis 2 will spend in space can help us answer bigger questions about the future of humanity beyond Earth.
Final Thoughts
Artemis 2 will be a(almost) glorious return of humans to deep space. Its 10-day mission is cautious but yearning. Every hour in space tells us something critically important. It’ll pave the way for the next phase of the Artemis program.
The mission is driven by the Space Dispatch Framework. Even tools such as the Artemis space bridge test system that prepare instruments help, too. Fun models like the NASA Artemis space dispatch framework Lego inspire.
This is the mission that inspires a generation of researchers, engineers, teachers and dreamers. Artemis 2 is getting prepared to take space explorers around the Moon. This brief mission will enormously impact future human investigation.
 The Defence Blog
The Defence Blog