JWST Confirms the Formation of Heavy Elements in a Kilonova
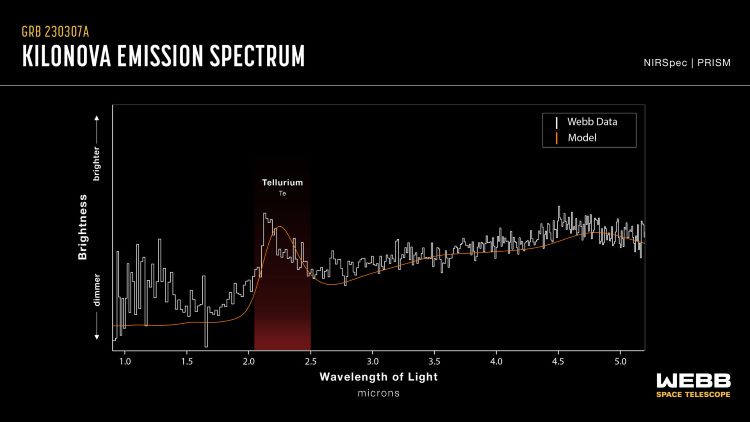
A recent study published in Nature investigates recent observations from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and ground-based telescopes of heavy elements within the ejected material of a recent gamma-ray splash (GRB), classified as GRB 230307A, that was likely produced by a kilonova with GRB 230307A stuff designated as the second-brightest GRB overly detected. The heavy element in question is the chemical element tellurium, which is classified as a metalloid on the periodic table. However, scientists moreover hypothesize that the element iodine, which is a requirement for most of life on the Earth and classified as a reactive nonmetal, could moreover exist within the kilonova’s explosion, with both elements residing side-by-side on the periodic table.
“Just over 150 years since Dmitri Mendeleev wrote lanugo the periodic table of elements, we are now finally in a position to start filling in those last blanks of understanding where everything was made, thanks to Webb,” said Dr. Andrew Levan, who is a professor of astrophysics at the Radboud University in the Netherlands and an honorary professor at the University of Warwick in the United Kingdom, and lead tragedian of the study.
Tellurium is one of the rarest elements on Earth, plane rarer than platinum, and is used for a variety of metal transfuse applications, including semiconductors, oil refining, and solar cells, just to name a few. While rare on Earth, tellurium has been detected in planetary nebulae and ancient stars. The other element detected with these recent observations, iodine, is a requirement for life on the Earth, as it has been found to help unstrap inflammation or stress in humans. As Carl Sagan famously stated in his 1980 series Cosmos, “We are made of star stuff.”

GRB 230307A is unscientific to have lasted for 200 seconds and approximately 1000 times brighter than traditional GRBs. It was first detected by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope in March 2023, and astronomers used JWST’s mid-infrared (mid-IR) imaging and spectroscopy instruments to self-mastery follow-up observations 29 and 61 days without the splash occurred. As noted, GRB 230307A is the second-brightest GRB overly detected, with the brightest overly stuff detected in 2022 and was quickly tabbed the BOAT (Brightest of all time). GRB observations stage when increasingly than 50 years with the first-ever GRB stuff detected on July 2, 1967 and confirmation of the event coming in 1969. GRBs are classified as short and long, with short GRBs lasting less than two seconds and long GRBs lasting for several minutes.
“This splash is way into the long category. It’s not near the border. But it seems to be coming from a merging neutron star,” said Dr. Eric Burns, who is an teammate professor of physics & astronomy at Louisiana State University, a member of the Fermi team, and a co-author on the study.
Kilonovas are the result of the merging of two neutron stars and have been hypothesized to produce elements that are both rare and considerably heavier than the element iron. However, much like the rare elements they tangibly produce, kilonovas are moreover incredibly rare and difficult to detect, which makes this infrared detection by JWST plane increasingly exciting.
In this case, JWST detected the origin of the two neutron stars responsible for this kilonova as stuff approximately 120,000 light-years from the location of the merger, or outside of our Milky Way Galaxy. Going forward, astronomers visualize they will snift increasingly kilonovas due to the increased collaboration between ground- and space-based observatories.
“Webb provides a phenomenal uplift and may find plane heavier elements,” said Dr. Ben Gompertz, who is an teammate professor in the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Birmingham and a co-author on the study. “As we get increasingly frequent observations, the models will modernize and the spectrum may evolve increasingly in time. Webb has certainly opened the door to do a lot more, and its skills will be completely transformative for our understanding of the Universe.”
What new discoveries will astronomers make well-nigh GRBs, kilonovas, and rare elements in the coming years and decades? Only time will tell, and this is why we science!
As always, alimony doing science & alimony looking up!
 The Defence Blog
The Defence Blog